The goal of the GRESB Assessments is to capture the most material ESG data related to the sustainability performance of real estate and infrastructure companies and assets. This data and the insights derived from it are used by investors to assess organizational exposure to various risks and to identify new opportunities to invest in strong-performing companies.
To remain fit for purpose, the GRESB Assessments are based on the independently owned and governed GRESB Standards, which are reviewed on an annual basis by the GRESB Foundation. This ensures that material ESG issues are addressed and covered by the GRESB Assessments as they develop and emerge. Part of this process is reviewing and mapping other important frameworks and standards to understand where and how the GRESB Standards may align.
Depending on the nature and goals of the various ESG frameworks reviewed, this annual alignment review may inform prioritization of ESG issues that are considered in the GRESB Standards as well as the approach taken for the technical implementation of any proposed changes. This is in addition to other contributions to the standards development process, which include stakeholder feedback, analysis of assessment results, market trends reviews, and technical research.
For a detailed description of the new governance structure, the GRESB Standards Development Process, and the changes for the 2023 GRESB Standards, as well as links to helpful resources, please visit this page.
Alignment with the GRESB Standards
Below are links to alignment documents for many of the most referenced ESG frameworks in use today.
| Real Estate | Infrastructure |
For each external framework, GRESB created an analysis table with the framework’s relevant indicators, which were mapped to specific indicators from the relevant GRESB’s standards. From this, GRESB analyzed the level of alignment between the GRESB indicators and those from the external framework, following the logic described in the downloadable excel files below. A GRESB partner was then asked to provide an independent third-party review of the alignment scores.
Overall framework alignment
While various frameworks were created for different purposes, analyzing and understanding the degree of alignment between the various frameworks used by the industry is helpful when considering potential changes and how one might reduce overall reporting burden. Therefore, a high or low degree of alignment is not a reflection on the value of a given framework.
Real Estate
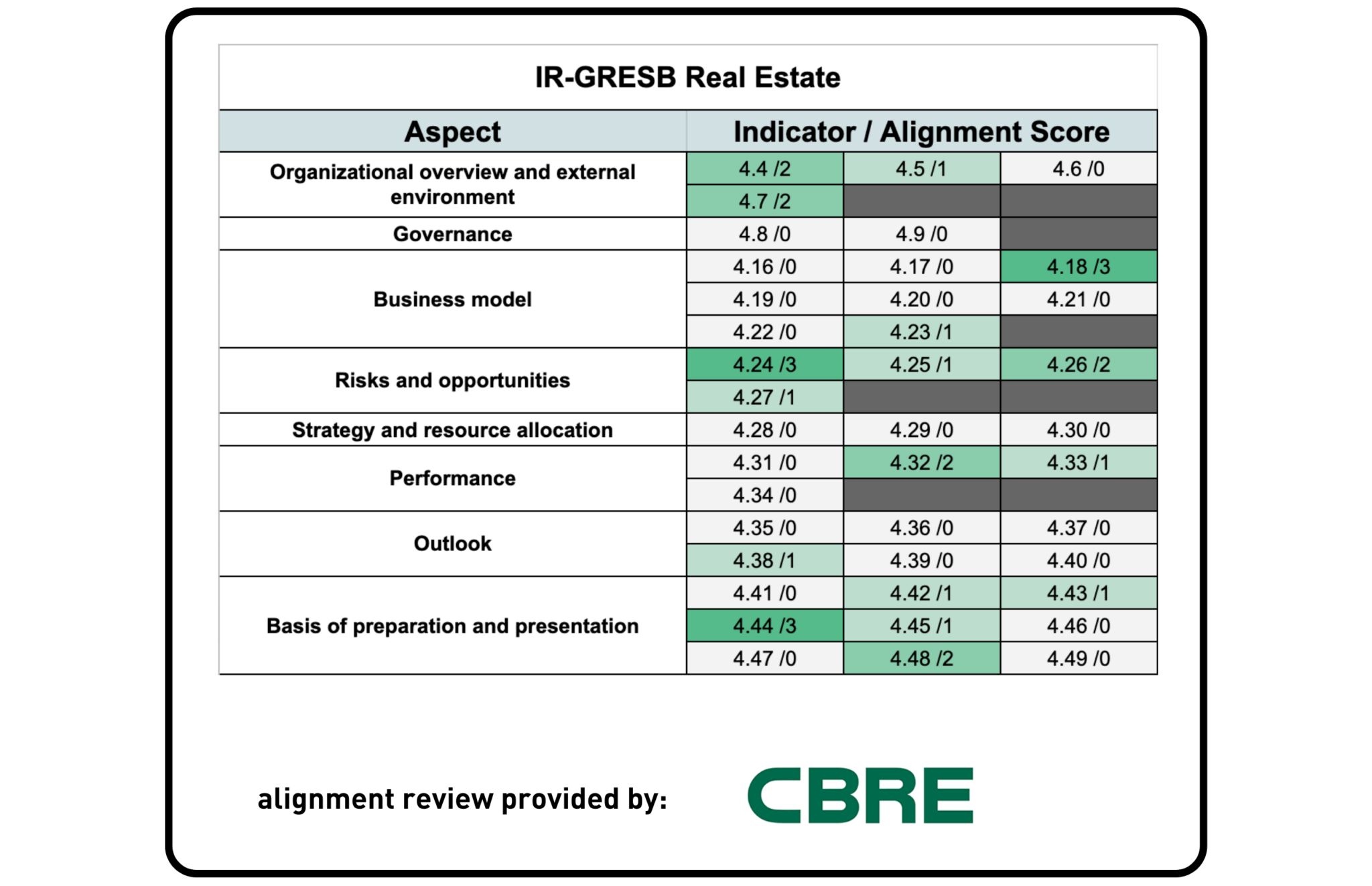
IR & GRESB
CBRE – the world’s leading commercial property and real estate services adviser that provides a comprehensive range of commercial property services to their clients – was asked to provide a third-party review of alignment between GRESB and the <IR> Framework.
Takeaway
While both frameworks were developed for different purposes, there is a degree of overall alignment, with several individual indicators being strongly aligned. <IR> provides ‘Guiding Principles and Content Elements that govern the overall content of an integrated report and to explain the fundamental concepts that underpin them.’ Meanwhile, the GRESB Standards provide specific, detailed, and replicable requirements for what should be reported for each ESG topic, including metrics. This ensures the information reported is comparable, consistent, and reliable across participants. The most significant areas of alignment are related to instance on disclosures covering Organizational overview and external environment, but there is no overlap on disclosures covering the management and/or performance of ESG topics.
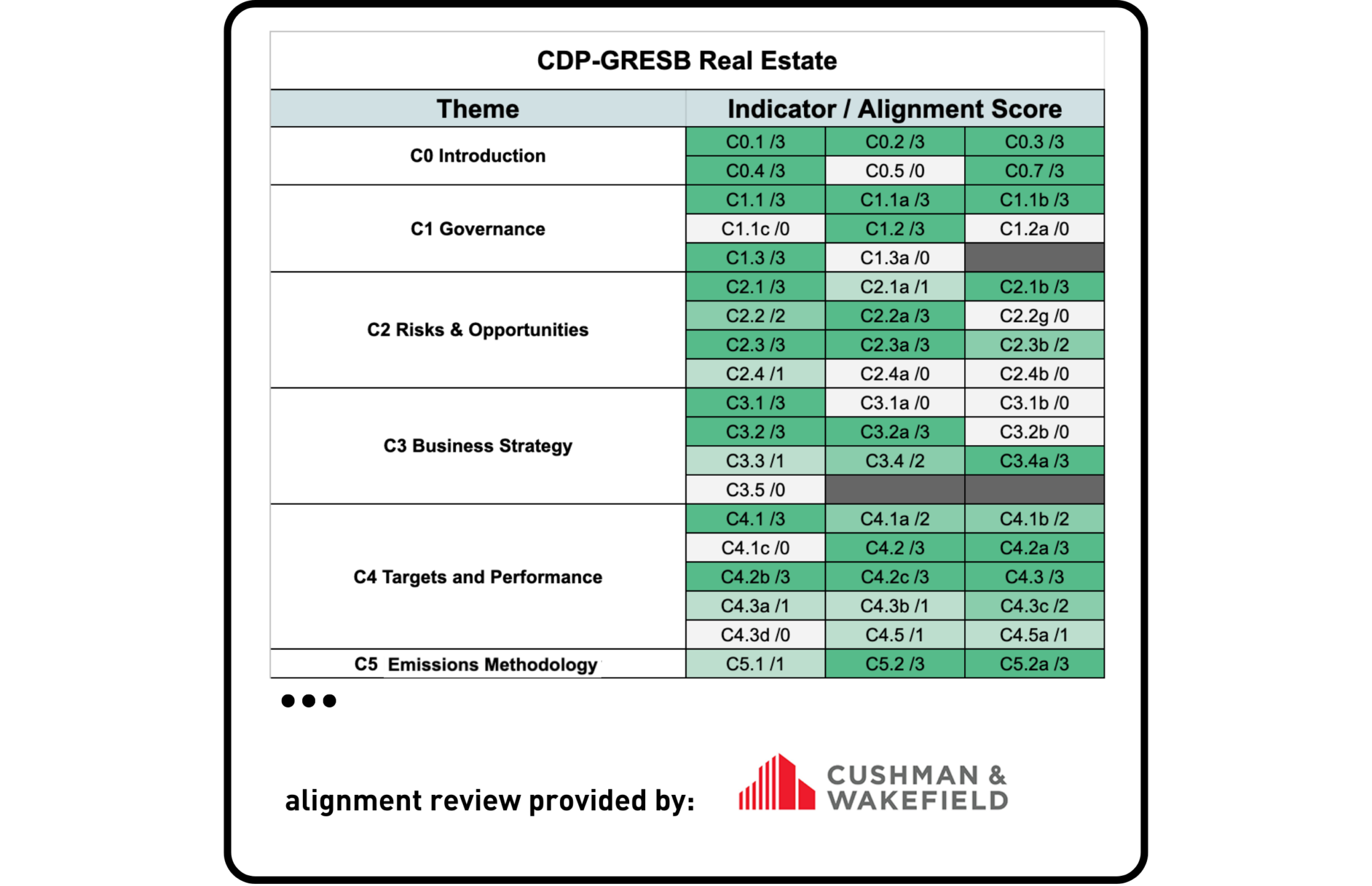
CDP & GRESB
Cushman & Wakefield, a leading global real estate services firm with 45,000 employees in more than 70 countries, was asked to provide a third-party review of the alignment between GRESB and CDP.
Takeaway
The CDP Climate Change 2021 Questionnaire focuses exclusively on climate-related disclosures, allowing to surface very granular information on the topic. Despite the difference in granularity, the analysis shows that the GRESB Real Estate Standard is significantly aligned with CDP.
Most alignment is observed between GRESB and the following CDP modules: Introduction (C0); Risks and Opportunities (C2); Business Strategy (C3); Targets and Performance (C4); Emissions Methodology (C5); Emissions Data (C6); and Verification (C10).
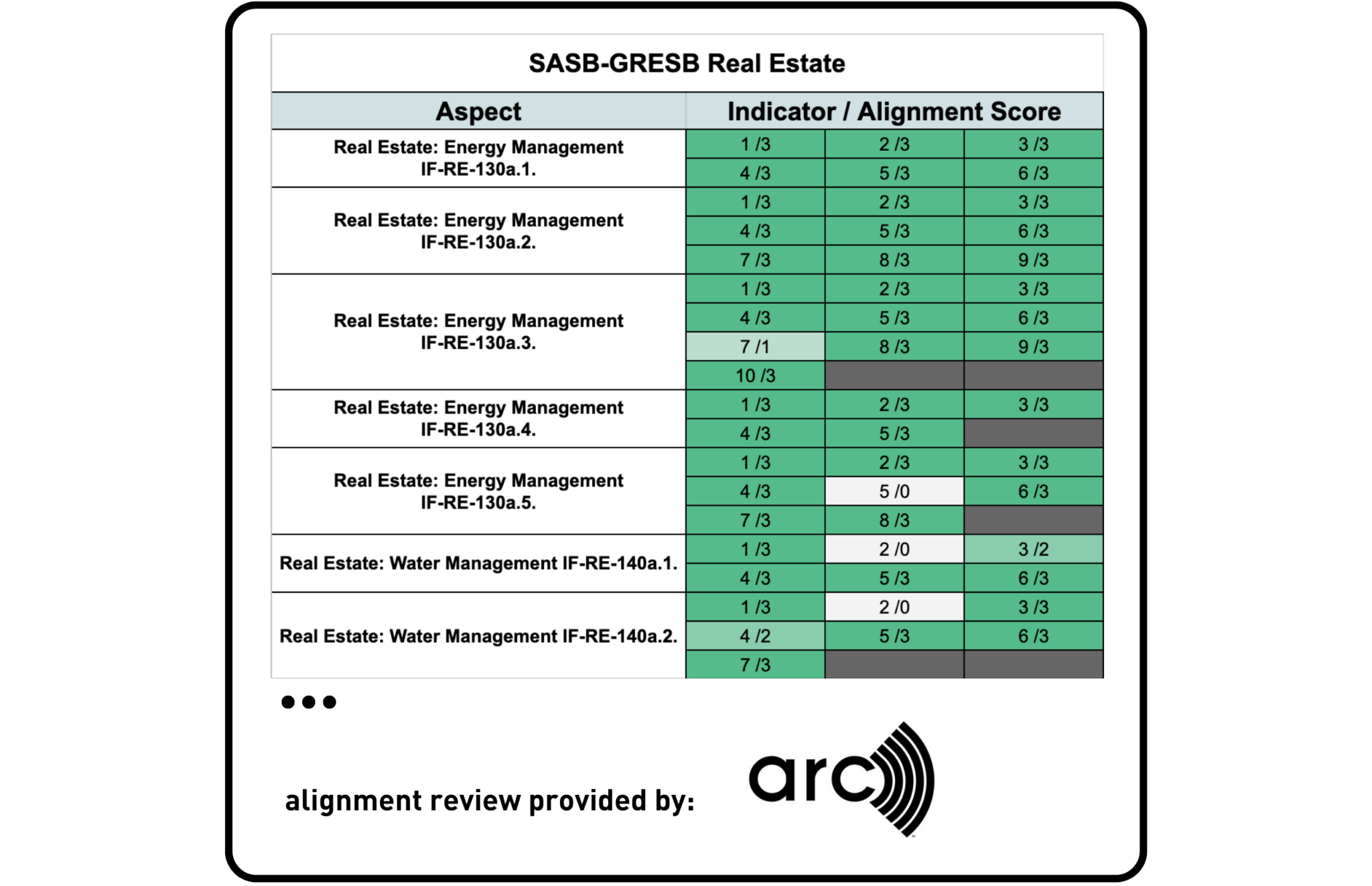
SASB & GRESB
Arc Skoru Inc. – a company that measures, tracks, and scores the operational performance of spaces, buildings, portfolios, and places around the world – provided a third-party review of the alignment between the GRESB Real Estate Standards and SASB.
Takeaway
Among all frameworks analyzed this year, SASB Standards and GRESB Standards showed the highest levels of alignment. The Real Estate SASB Standard (RE) & Real Estate Services SASB Standard (RS) were reviewed against the GRESB 2023 Real Estate Standards. The analysis found high alignment, with nearly 80% of SASB’s RE indicator objectives/scopes and underlying content addressed by GRESB. Significant alignment was also found between GRESB Standards and SASB’s RS Standard, with an overall alignment of nearly 70%.
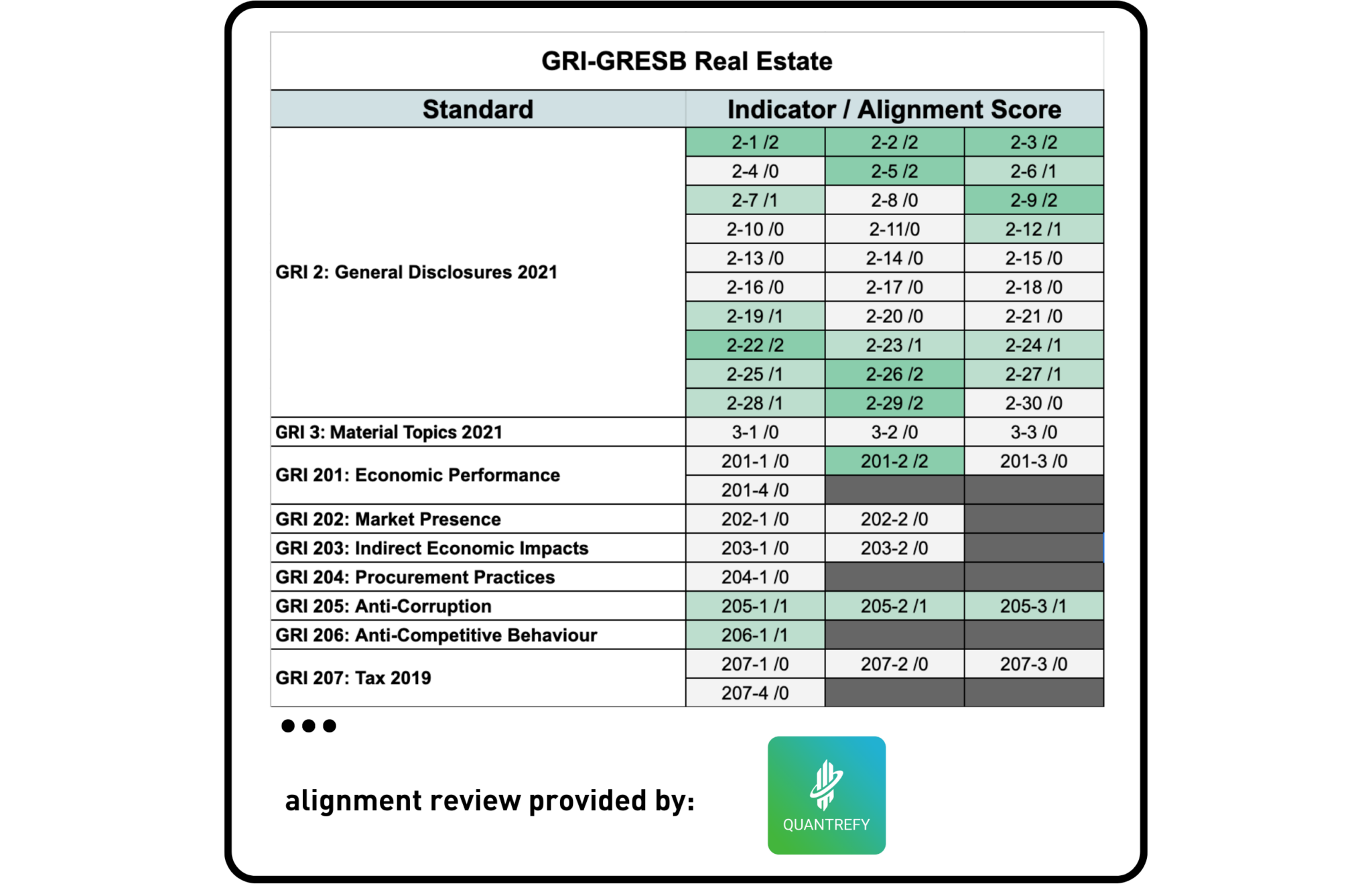
GRI & GRESB
QUANTREFY, the world’s first ESG implementation platform that supports asset and portfolio managers, was asked to provide a third-party review of the alignment between GRESB and GRI.
Takeaway
Much of the Universal and Topic-specific GRI Standards that were analyzed exceeds the scope of the GRESB Standards. In addition, some material topics in the GRESB Standards are sector-specific and hence not covered by GRI from a sector perspective (e.g. the GRESB Tenants/Occupiers aspect is specific to the real estate sector and not specifically covered by GRI Standards).
Overall there is an element of alignment between GRESB and GRI. The analysis shows that GRESB has a lower level of alignment with the GRI 1-2-3 Foundation 2021 Standards than with the GRI 300 Environmental Standards, which has a high degree of alignment by indicators. Lower alignment was found with the GRI 200 Economic Standards and GRI 400 Social Standards.
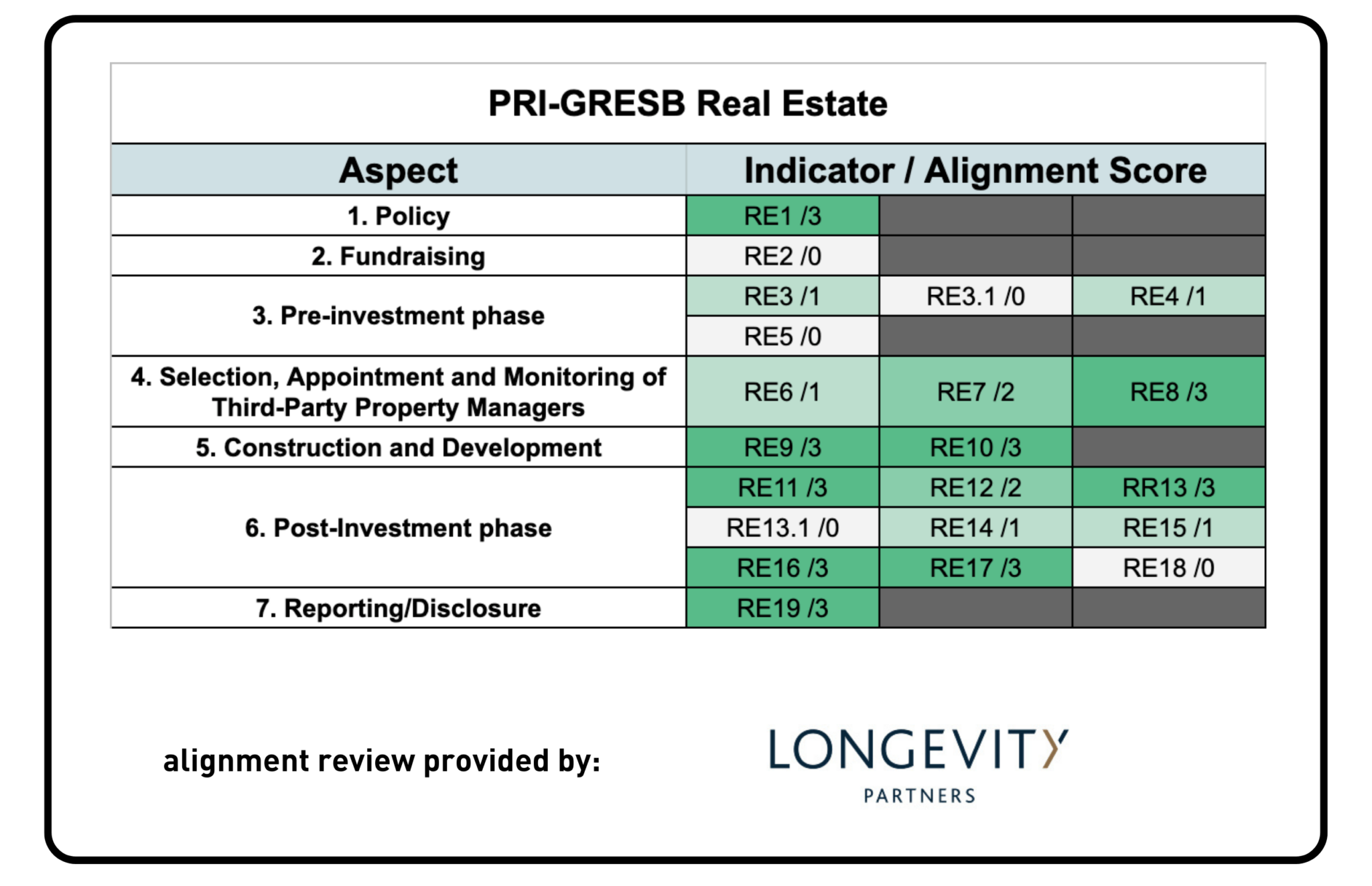
PRI & GRESB
Longevity Partners – a multi-disciplinary energy and sustainability consultancy that supports businesses in the transition to a low-carbon economy across the UK, Europe, and worldwide – was asked to provide a third-party review of GRESB’s alignment to PRI.
Takeaway
PRI Reporting Framework for Real Estate 2021 consists of just 19 indicators, with a scope applying to PRI signatories who invest directly – either individually or with other investors – in real estate via non-listed equity. This is in contrast to the GRESB Standards, which have significantly more indicators and a broader scope. For commonly relevant indicators, the analysis shows that the GRESB Real Estate Standard is significantly aligned with PRI.
Most alignment is observed between GRESB and the following PRI topics: Policy, Construction and Development; Reporting/Disclosure Post-Investment Phase and Selection; and Appointment and Monitoring of Third-Party Property Managers. No alignment was found between GRESB and PRI’s Fundraising and Pre-Investment Phase topics.
Infrastructure
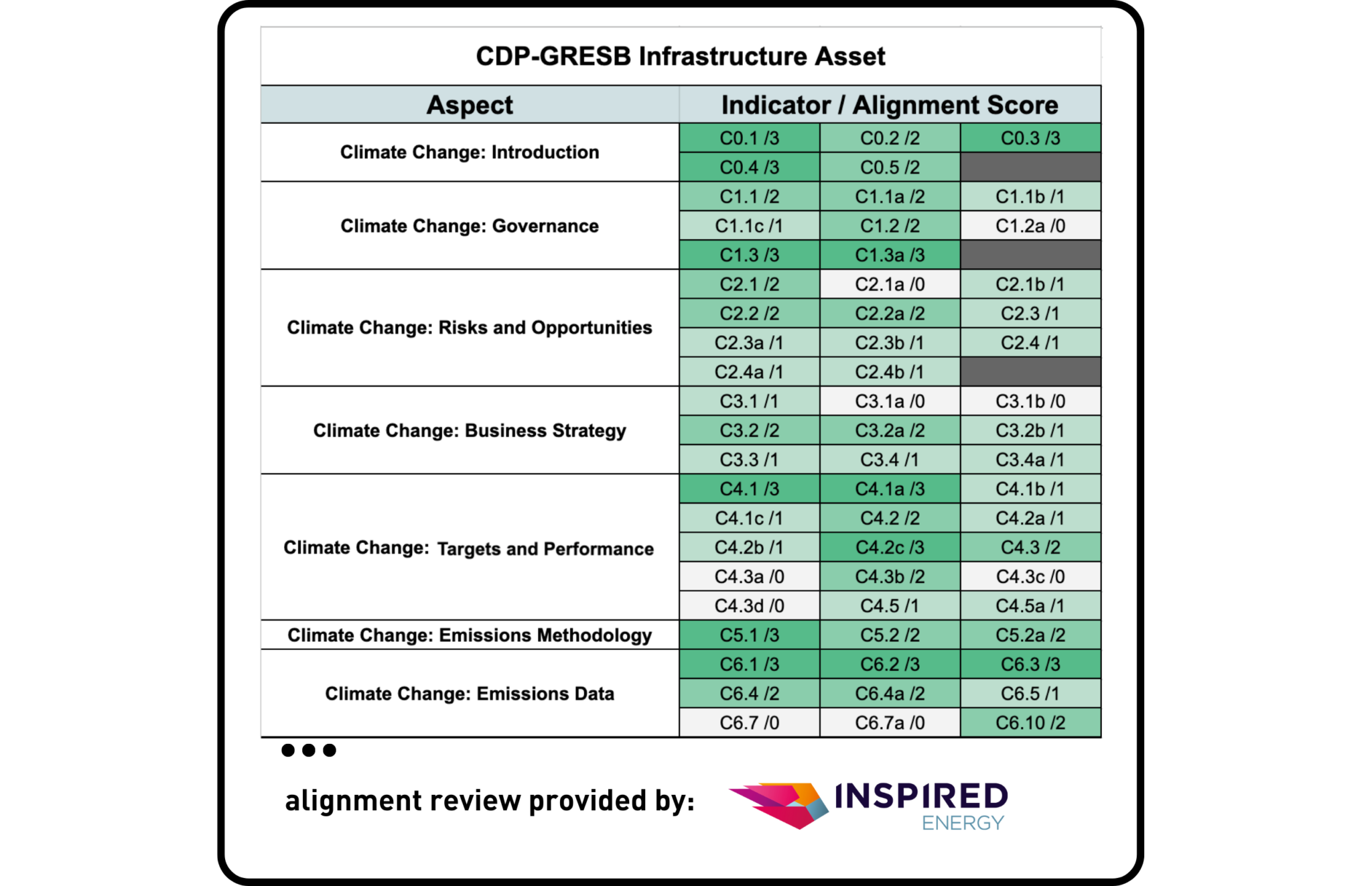
CDP & GRESB
Inspired Energy, one of the largest energy consultancies in the UK and now part of a group of companies within Inspired plc (INSE:LSE), was asked to provide a third-party review of the alignment exercise between GRESB and CDP.
Takeaway
The CDP Climate Change 2021 Questionnaire and the CDP Water Security 2021 Questionnaire were analyzed against GRESB’s 2023 Infrastructure Asset Standard. GRESB’s Standards are found to be partially aligned with the CDP Climate Change 2021 Questionnaire and the CDP Water Security 2021 Questionnaire. Similarly to the analysis done between both frameworks with real estate, the overall levels of alignment can be understood by the difference in scope of topics covered by CDP and GRESB. While CDP focuses on specific climate or environmental topics, GRESB’s scope is broader, explaining the difference in granularity of information that can be reported when using one or the other framework.
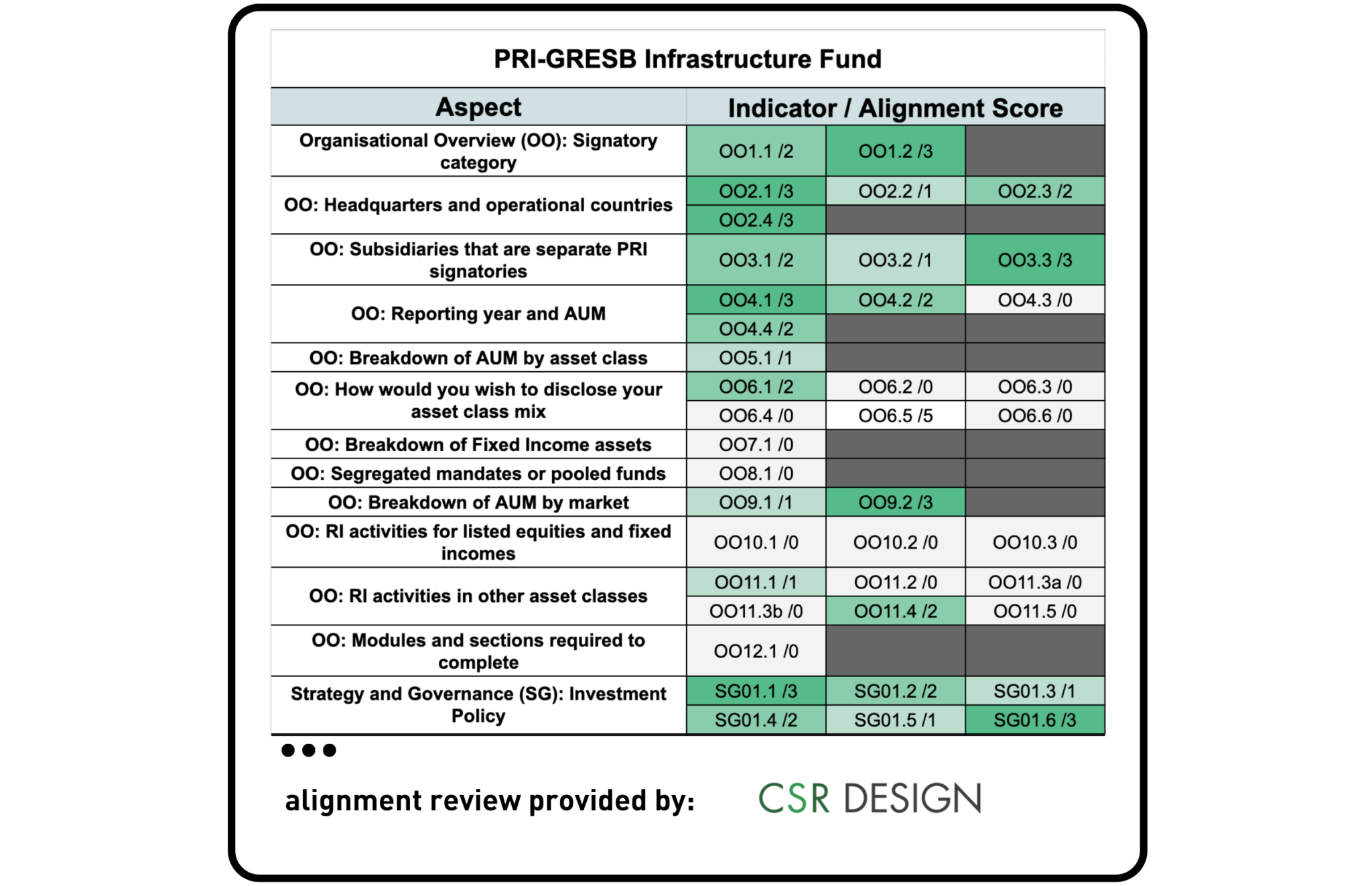
PRI & GRESB
CSR Design, a specialist consulting firm based in Japan that focuses on sustainability aspects in the real estate and infrastructure sectors, was asked to review the alignment between the GRESB Infrastructure Fund Standards and PRI.
Takeaway
PRI’s 2019 Reporting Framework was analyzed against GRESB’s 2022 Infrastructure Fund Assessment, showing partial alignment between GRESB and the following PRI modules: Organisation Overview; Strategy and Governance; and Infrastructure. The Appointment and Monitoring (SAM) module was less aligned, with roughly one in five indicators being directly addressed by GRESB. This perceived level of alignment is likely due to slight differences in the focus of both frameworks, such as GRESB’s Standard addressing some aspects of ESG management and investment processes but not demonstrating the implementation of responsible investment principles.
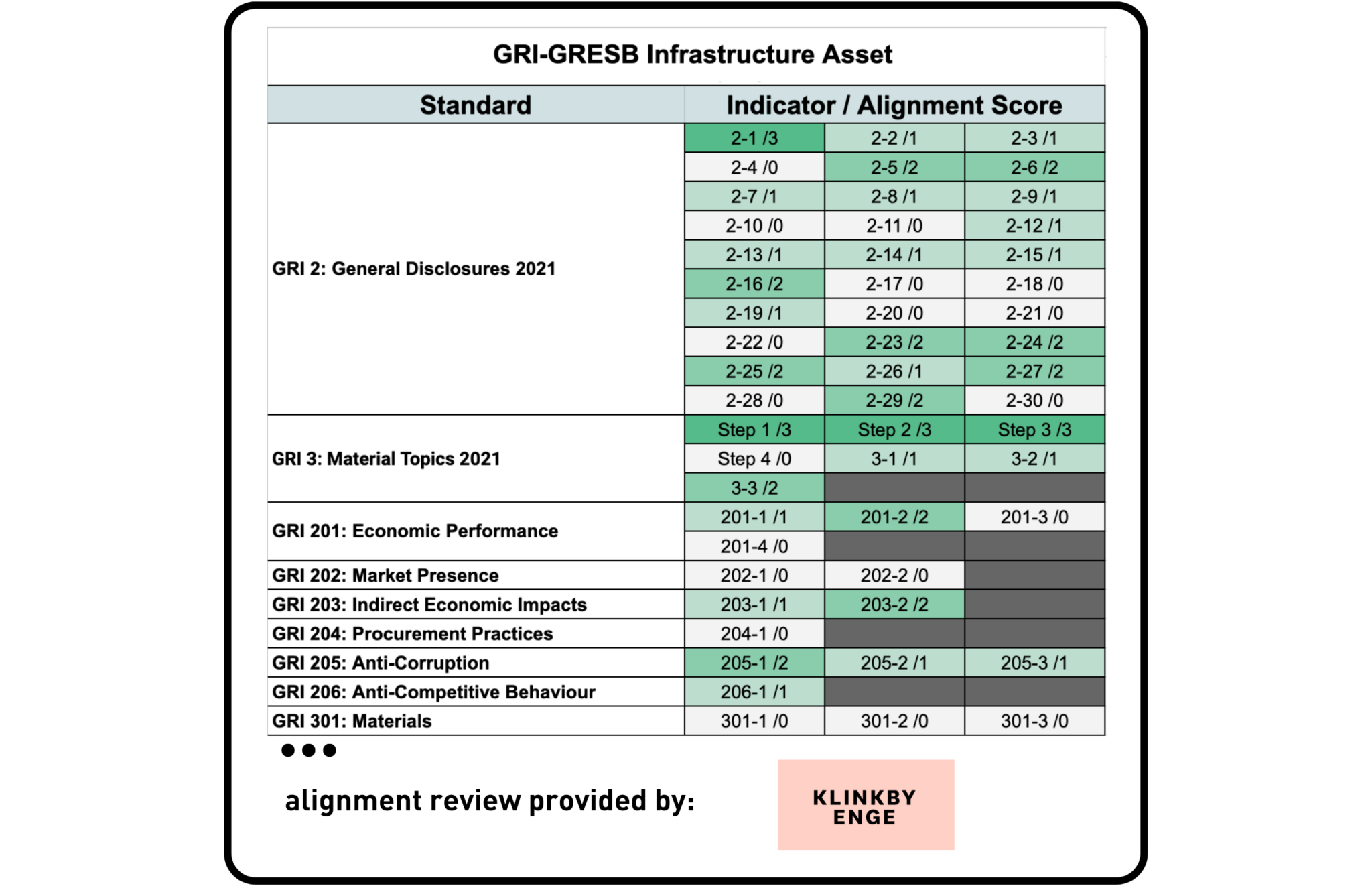
GRI & GRESB
Klinkby Enge – an independent advisory firm specialized in ESG due diligence, ESG data for private assets, and consulting on sustainable investing – was asked to provide a third-party alignment review of GRESB and GRI.
Takeaway
The GRI Universal Standards and Topic-Specific Standards series were analyzed against the GRESB Standards. Similarly to the analysis performed for real estate, the entire GRI Standards were mapped, much of which exceeds the scope of the GRESB Standards. In addition, some material topics in the GRESB standards are sector-specific, and hence not covered by GRI from a sector perspective. For example, the Customers aspect in the GRESB Infrastructure Asset Standards are specific to the infrastructure sector and so are not well covered by GRI’s standards. A partial overall framework alignment was observed between both frameworks. Most alignment between frameworks was observed on environmental topics.
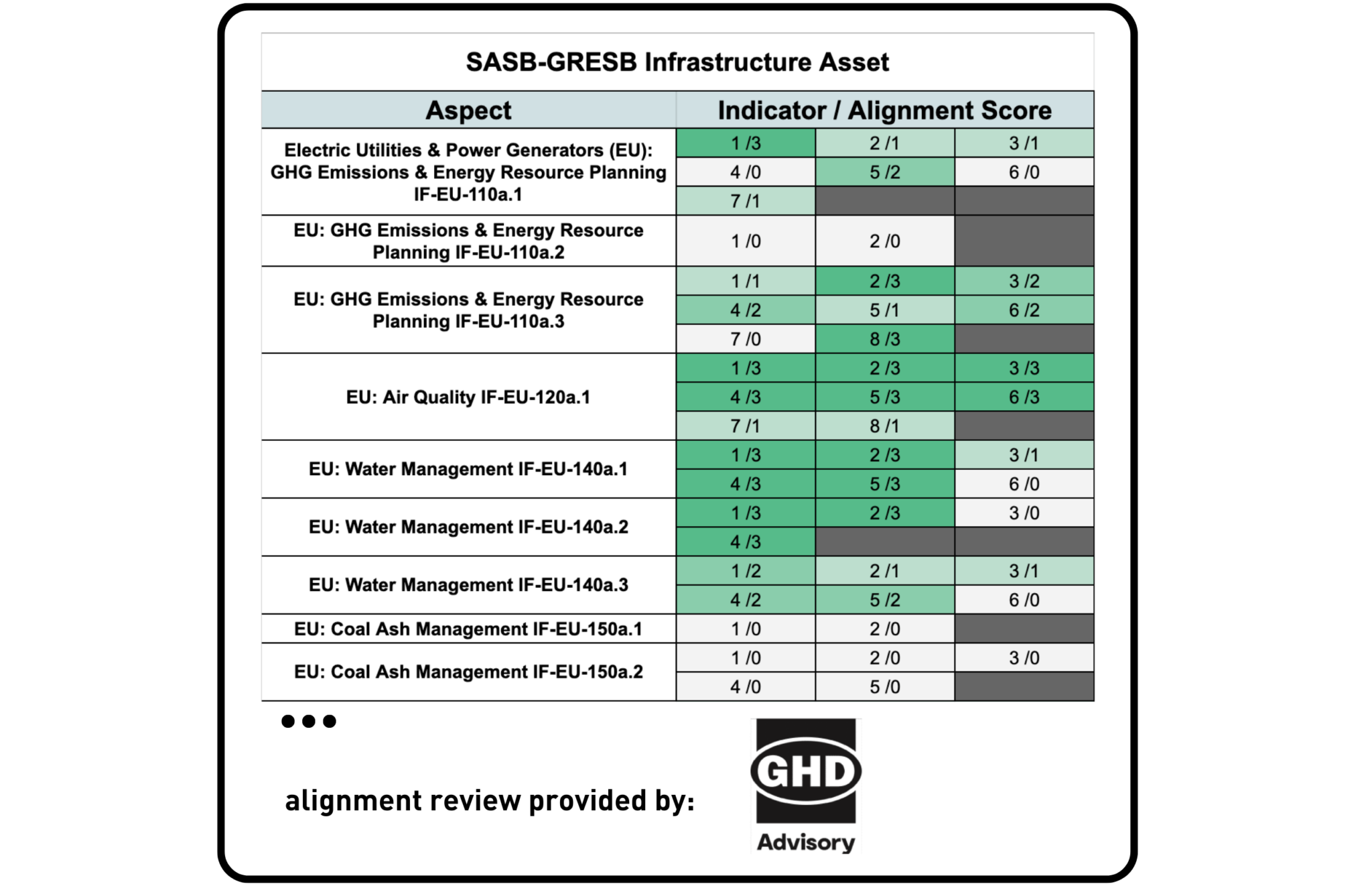
SASB & GRESB
GHD Advisory – one of the world’s leading professional services companies operating in the global markets of water, energy and resources, environment, property and buildings, and transportation – was asked to provide a third-party review of the level of alignment between GRESB and SASB.
Takeaway
Among all frameworks analyzed this year, the GRESB 2023 Infrastructure Asset Assessment and the SASB Standards showed some of the highest levels of alignment. SASB Standards reviewed included the Electric Utilities & Power Generators; Engineering & Construction Services; Gas Utilities & Distributors; Waste Management; and Water Utilities & Services, with partial alignment between both frameworks. This may be explained by the similar objectives pursued by both frameworks, which are to inform investment decision-making. Some differences may exist due to the fact that while GRESB ultimately seeks to score and benchmark, the SASB Standards emphasizes disclosure and transparency of ESG risks and opportunities, leading to a difference in the intent of the disclosures and reported information.
Chat with us about GRESB participation & other ESG frameworks
"*" indicates required fields